what happens in the three stages of the cell cycle Cell cycle regulation
The cell cycle is a fascinating and essential process that occurs in all living organisms. It is a series of events that take place in a cell, leading to its division and the formation of new cells. Understanding the cell cycle is crucial in various fields of science, including biology and medicine. In this post, we will explore the different stages of the cell cycle and their significance.
Cell Cycle Stages
 The cell cycle consists of several distinct stages, each with its own specific tasks and characteristics. These stages ensure the accurate duplication and distribution of genetic material in a cell. Let’s delve deeper into each stage:
The cell cycle consists of several distinct stages, each with its own specific tasks and characteristics. These stages ensure the accurate duplication and distribution of genetic material in a cell. Let’s delve deeper into each stage:
- Interphase
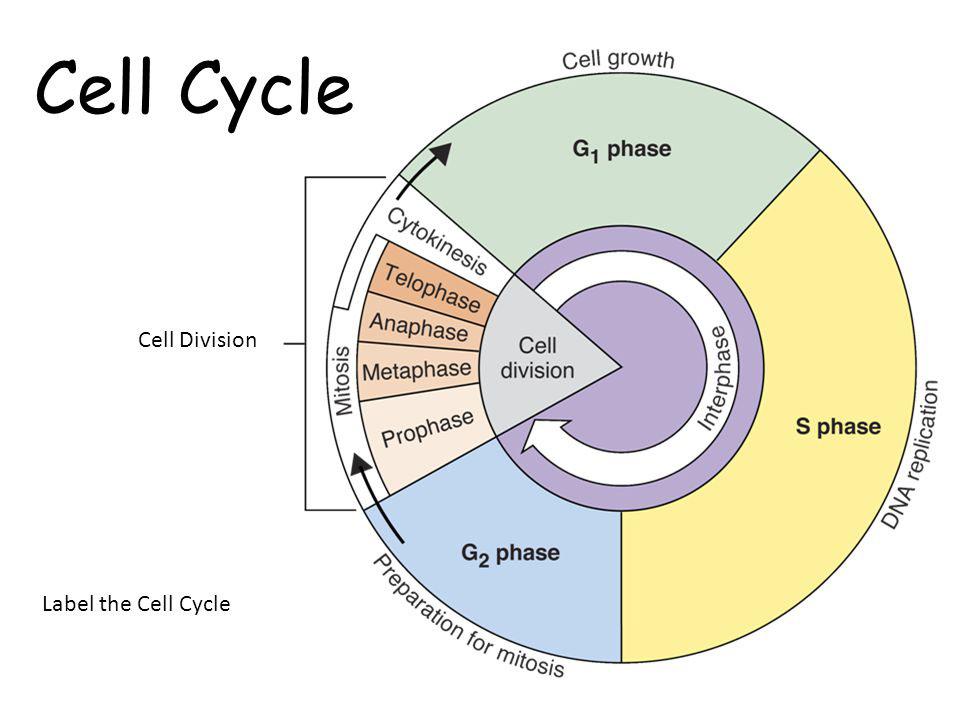 Interphase is the longest phase of the cell cycle, accounting for approximately 90% of the entire cycle. It is further divided into three subphases: G1 phase, S phase, and G2 phase.
Interphase is the longest phase of the cell cycle, accounting for approximately 90% of the entire cycle. It is further divided into three subphases: G1 phase, S phase, and G2 phase.
G1 Phase:
This is the first gap phase, during which the cell grows in size and carries out its normal functions. It prepares itself for DNA replication and checks for any errors or damage in the DNA. Once the cell passes the G1 checkpoint, it enters the S phase.
S Phase:
In the synthesis phase, the cell synthesizes a copy of each chromosome through DNA replication. This ensures that each new daughter cell will receive an identical set of genetic material.
G2 Phase:
The second gap phase follows DNA replication, during which the cell continues to grow and prepares for cell division. It checks for any errors introduced during DNA replication and ensures that the cell is ready for mitosis.
- Mitosis
Mitosis is the phase of the cell cycle where the nucleus divides, leading to the formation of two identical daughter nuclei. It is further divided into four distinct stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
Prophase:
In prophase, the chromatin condenses and becomes visible as distinct chromosomes. The nuclear envelope starts to break down, and the mitotic spindle begins to form. The chromosomes become attached to the spindle fibers.
Metaphase:
During metaphase, the chromosomes align themselves along the equator of the cell, known as the metaphase plate. This alignment ensures that each daughter cell receives an equal number of chromosomes during division.
Anaphase:
In anaphase, the sister chromatids of each chromosome separate from each other and move towards opposite poles of the cell. This ensures that each daughter cell will have a complete set of chromosomes.
Telophase:
During telophase, the nuclear envelope reforms around the separated chromatids, forming two distinct nuclei. The chromosomes begin to decondense, and the mitotic spindle starts to disassemble. Telophase is followed by cytokinesis, the final stage of the cell cycle.
- Cytokinesis
Cytokinesis involves the physical division of the cell, resulting in two separate daughter cells. In animal cells, a cleavage furrow forms and deepens until the cell eventually pinches into two. In plant cells, a cell plate forms in the middle of the cell, which eventually develops into a new cell wall that separates the two daughter cells.
Understanding the stages of the cell cycle is crucial for various reasons. It allows scientists and researchers to study and manipulate cell division, aiding in the development of treatments for diseases such as cancer. Additionally, understanding the cell cycle’s intricacies helps us comprehend how new cells are formed and how organisms grow.
So next time you observe a dividing cell, take a moment to appreciate the intricate processes occurring within it. The cell cycle is a remarkable phenomenon that illustrates the remarkable complexity of life on our planet.
If you are looking for The Cell Cycle - Interphase & Mitosis | A-Level Biology Revision Notes you’ve came to the right page. We have 5 Pictures about The Cell Cycle - Interphase & Mitosis | A-Level Biology Revision Notes like Cell Cycle Stages And Description - Cell Cycle, The Cell Cycle - Interphase & Mitosis | A-Level Biology Revision Notes and also The Cell Cycle - Interphase & Mitosis | A-Level Biology Revision Notes. Here it is:
The Cell Cycle - Interphase & Mitosis | A-Level Biology Revision Notes
 alevelbiology.co.ukinterphase cycle cell mitosis division cells eukaryotic biology phases during happens events stages diagram kind meiosis pdf prophase main figure
alevelbiology.co.ukinterphase cycle cell mitosis division cells eukaryotic biology phases during happens events stages diagram kind meiosis pdf prophase main figure
The Cell Cycle - Phases - Mitosis - Regulation - TeachMePhysiology
 teachmephysiology.comcycle cell phases mitosis
teachmephysiology.comcycle cell phases mitosis
Cell Cycle Stages And Description - Cell Cycle
 cellcycleinfo.blogspot.commitosis fundamental processes quizizz
cellcycleinfo.blogspot.commitosis fundamental processes quizizz
Phases Of Cell Cycle - Online Biology Notes
 www.onlinebiologynotes.comcycle cell phases division synthesis biology mitosis cells notes phase g2 interphase growth protein which two ncert solutions made dna
www.onlinebiologynotes.comcycle cell phases division synthesis biology mitosis cells notes phase g2 interphase growth protein which two ncert solutions made dna
Cell Cycle Regulation - Mrs. Smith
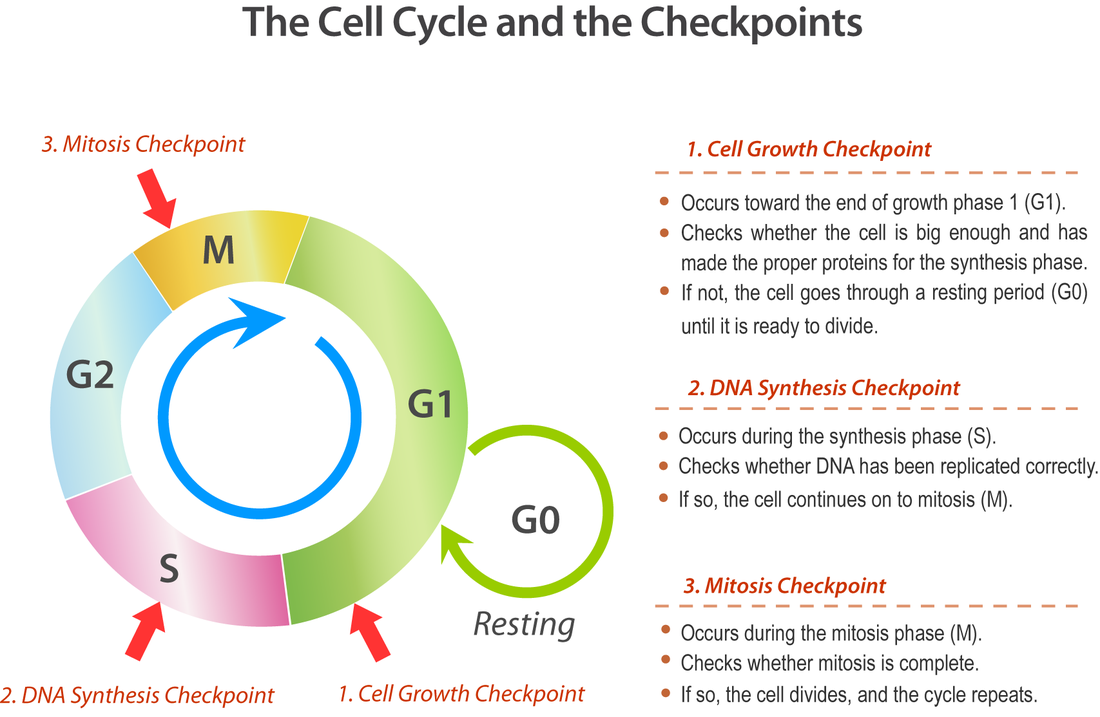 smithbiologypap.weebly.comcycle cell checkpoints biology mitosis phase division regulation eukaryotic different checkpoint g1 check control during which dna three g0 growth
smithbiologypap.weebly.comcycle cell checkpoints biology mitosis phase division regulation eukaryotic different checkpoint g1 check control during which dna three g0 growth
Interphase cycle cell mitosis division cells eukaryotic biology phases during happens events stages diagram kind meiosis pdf prophase main figure. Phases of cell cycle. Cycle cell checkpoints biology mitosis phase division regulation eukaryotic different checkpoint g1 check control during which dna three g0 growth